From January 20 to November 10, 2021, Kaspersky experts uncovered a new piece of malware that has targeted more than 35,000 computers across 195 countries. Dubbed “PseudoManuscrypt” for its similarities with the advanced persistent threat (APT) group Lazarus’ Manuscrypt malware, this new malware contains advanced spying capabilities and has been seen targeting both government organisations and industrial control systems (ICS) across numerous industries.
Industrial organisations are some of the most coveted targets for cybercriminals – both for financial gain and intelligence gathering. In fact, 2021 saw significant interest in industrial organisations from well-known APT groups like Lazarus and APT41. While investigating another string of attacks, Kaspersky experts uncovered a new piece of malware with some similarities to Lazarus’ “Manuscrypt”, custom malware used in the group’s ThreatNeedle campaign against the defense industry. Hence, they dubbed it PseudoManuscrypt.
From January 20 to November 10, 2021, Kaspersky products blocked PseudoManuscrypt on more than 35,000 computers in 195 countries. Many of the targets were industrial and government organisations, including military-industrial enterprises and research laboratories. 7.2% of attacked computers were part of industrial control systems (ICS), with engineering and building automation representing the most affected industries.
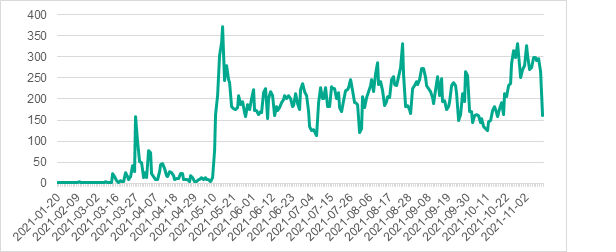
Number of systems on which PseudoManuscrypt was detected, by day
PseudoManuscrypt is initially
downloaded on targets’ systems via fake pirated software installer archives, some of which are for ICS-specific pirated software.
It is likely these fake installers are offered via a Malware-as-a-Service
(MaaS) platform. Curiously, in some cases, PseudoManuscrypt was installed via
the infamous Glupteba botnet. After initial infection, a complicated
infection chain is initiated that eventually downloads the main malicious module.
Kaspersky experts have identified two variants of this module. Both are capable
of advanced spyware capabilities, including logging keystrokes, copying data
from the clipboard, stealing VPN (and potentially RDP) authentication
credentials and connection data, copying screenshots, etc.
The attacks show no preference for particular industries, however, the large number of engineering computers attacked, including systems used for 3D and physical modeling and digital twins, suggest that industrial espionage may be one objective.
Oddly enough, some of the victims share ties with the victims of the Lazarus campaign ICS CERT previously reported on, and data is sent to the attackers’ server over a rare protocol using a library that has previously only been used with APT41’s malware. Nevertheless, given the large number of victims and the lack of an explicit focus, Kaspersky does not link the campaign to Lazarus or any known APT threat actor.
“This is a highly unusual campaign, and we are still piecing together the various information we have. However, one fact is clear: this is a threat that specialists need to pay attention to. It has been able to make its way onto thousands of ICS computers, including many high-profile organisations. We will be continuing our investigations, keeping the security community apprised any new findings,” commentsVyacheslav Kopeytsev, security expert at Kaspersky.
Read more about the PseudoManuscrypt campaign on ICS CERT.
To stay safe from PseudoManuscrypt, Kaspersky experts recommend organisations:
- Install endpoint protection software on all servers and workstations
- Check that all endpoint protection components are enabled on all systems and that a policy is in place which requires the administrator password be entered in the event someone attempts to disable the software.
- Check that Active Directory policies include restrictions on user attempts to log in to systems. Users should only be allowed to log in to those systems which they need to access to perform their job responsibilities.
- Restrict network connections, including VPN, between systems on the OT network; block connections on all those ports that are not required for the continuity and safety of operations.
- Use smart cards (tokens) or one-time codes as the second authentication factor when establishing a VPN connection. In cases where this is applicable, use the Access Control List (ACL) technology to restrict the list of IP addresses from which a VPN connection can be initiated.
- Train employees of the enterprise in working with the internet, email and other communication channels securely and, specifically, explain the possible consequences of downloading and executing files from unverified sources.
- Use accounts with local administrator and domain administrator privileges only when this is necessary to perform job responsibilities.
- Consider using Managed Detection and Response class services to gain quick access to high-level knowledge and the expertise of security professionals.
- Use dedicated protection for shop-floor systems. Kaspersky Industrial CyberSecurity protects industrial endpoints and enables OT network monitoring to identify and block malicious activity.
About Kaspersky ICS CERT
Kaspersky Industrial Control Systems Cyber Emergency Response Team (Kaspersky ICS CERT) is a global project launched by Kaspersky in 2016 to coordinate the efforts of automation system vendors, industrial facility owners and operators, and IT security researchers to protect industrial enterprises from cyberattacks. Kaspersky ICS CERT devotes its efforts primarily to identifying potential and existing threats that target industrial automation systems and the Industrial Internet of Things. Kaspersky ICS CERT is an active member and partner of leading international organisations that develop recommendations on protecting industrial enterprises from cyberthreats. ics-cert.kaspersky.com
